Contents
Bitcoin is a digital currency
Bitcoin(abbreviated as BTC) is a digital currency which you can send to others on the bitcoin’s network without the permission for intermediaries from any institution like banks or administrators. That is to say, Bitcoin, a completely and purely peer-to-peer electronic cash, allows online payments to be sent directly from one party to another without any limitations from a financial institution. Besides, the transactions made for Bitcoin are all verified by network nodes through cryptography, also recorded in a public distributed ledger called a blockchain that everyone has the transparent access to.
In 2008, Bitcoin was invented by an unknown person or group of people named Satoshi Nakamoto as a type of cryptocurrency, and publish the whitepaper – A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System. The person or group who created Bitcoin is still a mystery until now.


Bitcoin is running through a system referred to as“nodes” and “miners”, a collection of computers, that all run bitcoin’s code and store in blockchain, which can be thought of as a collection of blocks and in each block there is a collection of transactions. All the computers running the blockchain have the same list of blocks and transactions, and can transparently see these new blocks being developed with new bitcoin transactions, so no one can cheat or falsify the system, which provides a kind of top security.
Bitcoin system — Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System


Bitcoin is one of the first digital currencies based on peer-to-peer technology to accelerate the development of instant payments. The independent individuals and parties who own the governing computing power and participate in the bitcoin network are called bitcoin “miners” who are in charge of processing the transactions on the blockchain. They are also rewarded with the release of new bitcoin and transaction fees paid in bitcoin.
These miners mentioned above can be honored as the decentralized authority, who are enforcing the credibility security of the bitcoin network. New bitcoin is released to the miners at a fixed, but periodically declining rate.
In this way, bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies operate much differently from fiat currency; in traditional centralized banking systems, the currency is released at a rate matching the growth in goods, which is intended to maintain price stability. However, the decentralized system, like bitcoin, sets the release rate ahead of time and according to an algorithm.
Bitcoin Mining


Bitcoin mining is the process that bitcoin gets released into circulation. Generally, mining requires miners to solve the computationally difficult puzzles to discover a new block where data of Bitcoin network are permanently recorded, which is going to be added to the blockchain.
Bitcoin mining stores and verifies transaction records across the network. Miners are also rewarded with some bitcoin; the reward will get halved every 210,000 blocks ( About 4 years). The block reward was 50 new bitcoins in 2009. On May 11th, 2020, the third halving occurred, bringing the reward for each block discovery down to 6.25 bitcoins.
Normally miners will use many kinds of hardware to mine bitcoin. Some good and advanced devices can make higher rewards than others, such as Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASIC), and more advanced processing units, like Graphic Processing Units (GPUs), can win more rewards. These elaborate mining processors are known as “mining rigs.”
Bitcoin Halving


As we mentioned, miners will get rewarded with Bitcoin for verifying blocks of transactions. This reward will be cut in half every 210,000 blocks about every four years, which is called the bitcoin halving. The system is built-in with a deflationary setting, which can keep the rate that new Bitcoin is released into circulation.
The rewards for bitcoin mining will continue until about 2140. Once all bitcoin is mined from the code and all halvings are finished, the miners can still take the fees that they will charge network users who do the Bitcoin transactions. The hope is that healthy competition will keep fees low.
This system keeps Bitcoin’s stock-to-flow ratio and lowers its inflation until it is eventually zero. After the third halving that took place on May 11th, 2020, the reward for each block mined is now 6.25 Bitcoins.
The Blockchain
Bitcoin is a network running on a protocol known as the blockchain, which is most simply defined as a decentralized, distributed ledger that records the provenance of a digital asset. In 2008, a paper by a person or people called themselves Satoshi Nakamoto first described both the blockchain and Bitcoin.
The blockchain has since evolved into a separate concept, and thousands of blockchains have been created using similar cryptographic techniques. Blockchain sometimes refers to the original Bitcoin blockchain. At other times it refers to blockchain technology in general, or any other specific blockchain, such as Ethereum.
The basics of blockchain technology are mercifully straightforward. Any given blockchain consists of a single chain of discrete blocks of information, arranged chronologically. In principle this information can be any string of 1s and 0s, meaning it could include emails, contracts, land titles, marriage certificates, or bond trades. In theory, any type of contract between two parties can be established on a blockchain as long as both parties agree on the contract. This takes away any need for a third party to be involved in any contract. This opens a world of possibilities including peer-to-peer financial products, like loans or decentralized savings and checking accounts, where banks or any intermediary is irrelevant.
Who Is Satoshi Nakamoto?


Until now no one knows who invented bitcoin, or at least not conclusively. Satoshi Nakamoto is the name associated with the person or group of people who released the original bitcoin whitepaper in 2008 and worked on the original bitcoin software that was released in 2009. In the years since that time, many individuals have either claimed to be or have been suggested as the real-life people behind the pseudonym, but as of June 2021, the true identity (or identities) behind Satoshi remains obscured.
There are a few possible motivations for bitcoin’s inventors deciding to keep their identity secret. One is privacy: As bitcoin has gained in popularity, and becomes something of a worldwide phenomenon. Satoshi Nakamoto would likely garner a lot of attention from the media and from governments.
Another reason could be the potential for bitcoin to cause a major disruption in the current banking and monetary systems. If bitcoin were to gain mass adoption, the system could surpass nations’ sovereign fiat currencies. This threat to existing currency could motivate governments to want to take legal action against bitcoin’s creator.
The other reason is safety. Looking at 2009 alone, 32,489 blocks were mined; at the reward rate of 50 bitcoin per block, the total payout in 2009 was 1,624,500 bitcoin. One may conclude that only Satoshi and perhaps a few other people were mining through 2009 and that they possess a majority of that stash of bitcoin.
Someone in possession of that much bitcoin could become a target of criminals, especially since bitcoin is less like stocks and more like cash, where the private keys needed to authorize spending could be printed out and literally kept under a mattress. While it’s likely the inventor of bitcoin would take precautions to make any extortion-induced transfers traceable, remaining anonymous is a good way for Satoshi to limit exposure.
How Does Bitcoin Work?
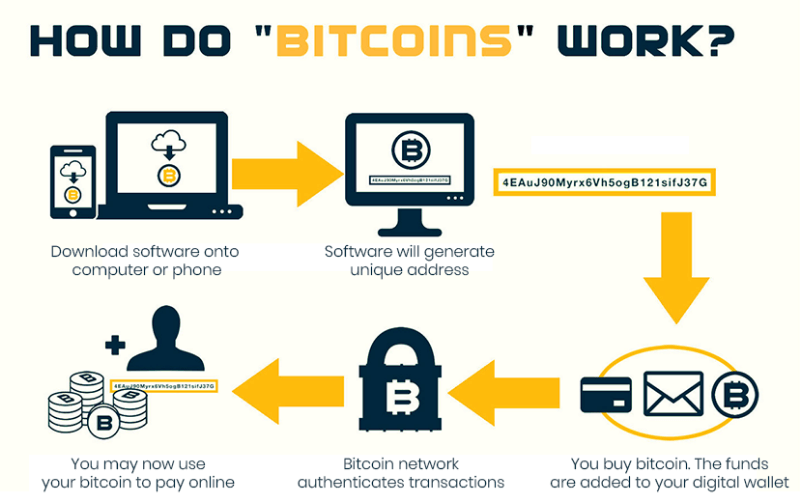

Bitcoin is kind of software, a purely digital phenomenon, a set of protocols and processes. It also is the most successful of hundreds of attempts to create virtual money through the use of cryptography, the science of making and breaking codes. Bitcoin has inspired hundreds of imitators, but it remains the largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization, a distinction it has held throughout its decade-plus history.
Bitcoin is built on a distributed digital record called a blockchain. As the name implies, blockchain is a linked body of data, made up of units called blocks that contain information about each and every transaction, including date and time, total value, buyer and seller, and a unique identifying code for each exchange. Entries are strung together in chronological order, creating a digital chain of blocks.
Once a block is added to the blockchain, it becomes accessible to anyone who wishes to view it.While the idea that anyone can edit the blockchain might sound risky, it’s actually what makes Bitcoin trustworthy and secure. In order for a transaction block to be added to the Bitcoin blockchain, it must be verified by the majority of all Bitcoin holders, and the unique codes used to recognize users’ wallets and transactions must conform to the right encryption pattern.
These codes are long, random numbers, making them incredibly difficult to fraudulently produce. In fact, a fraudster guessing the key code to your Bitcoin wallet has roughly the same odds as someone winning a Powerball lottery nine times in a row. This level of statistical randomness blockchain verification codes, which are needed for every transaction, greatly reduces the risk anyone can make fraudulent Bitcoin transactions.
How to buy Bitcoin?


Most people buy Bitcoin via exchanges, such as Coinbase. Exchanges allow you to buy, sell and hold cryptocurrency, and setting up an account is similar to opening a brokerage account — you’ll need to verify your identity and provide some kind of funding source, such as a bank account or debit card.
Major exchanges include Coinbase, Kraken, and Gemini. You can also buy Bitcoin at a broker like Robinhood.
Pionex provides 13 free trading bots for its users. It helps retail investors control their risks while trading crypto. Check out Pionex here.
Regardless of where you buy your Bitcoin, you’ll need a digital wallet in which to store it. This might be what’s called a hot wallet or a cold wallet. A hot wallet (also called an online wallet) is stored by an exchange or a provider in the cloud. Providers of online wallets include Exodus, Electrum and Mycelium. A cold wallet (or mobile wallet) is an offline device used to store Bitcoin and is not connected to the Internet. Some mobile wallet options include Trezor and Ledger.
A few important notes about buying Bitcoin: While Bitcoin is expensive, you can buy fractional Bitcoin from some vendors. You’ll also need to look out for fees, which are generally small percentages of your crypto transaction amount but can really add up on small-dollar purchases. Finally, be aware that Bitcoin purchases are not instantaneous like many other equity purchases seemingly are. Because Bitcoin transactions must be verified by miners, it may take you at least 10–20 minutes to see your Bitcoin purchase in your account.
How does Bitcoin make money?
Bitcoin value follows the law of supply and demand — and because demand waxes and wanes, there’s a lot of volatility in the cryptocurrency’s price.
Besides mining bitcoin, which requires technical expertise and an investment in high-performance computers, most people purchase bitcoins as a form of currency speculation — betting that the U.S. dollar value of one bitcoin will be higher in the future than it is today. But that’s difficult to predict.